Managing employee data can be overwhelming, especially with all the information HR professionals handle daily. This is where HRIS, or Human Resource Information System, steps in as an essential tool. No longer do you have to dig through endless stacks of paperwork to find what you need. An HRIS, combined with proper HRIS training, makes storing, organizing, and accessing employee information quick and easy, ensuring you maximize its full potential.
With improvements in technology, HRIS systems have become a must-have for businesses, offering customized solutions to meet various needs. Whether you’re an experienced HR manager or just starting out, knowing how to use an HRIS is crucial for keeping up in today’s workplace. This guide will help you understand what an HRIS does and how it can simplify your daily tasks.
Let’s explore how HRIS can make your job easier!
What is an HRIS?
A Human Resource Information System (HRIS) is a specialized software application that helps organizations manage their employee data effectively. Think of it as the digital hub for all things related to HR, where information about employees, company policies, and processes is stored and accessed. With proper HRIS training, you can efficiently centralize this data, streamlining administrative tasks and making it easier for HR professionals to focus on more strategic activities.
An HRIS simplifies complex HR tasks such as recruiting, onboarding, payroll processing, and benefits administration. This HR automation not only reduces the chance of errors but also ensures compliance with company policies and legal requirements. In short, an HRIS is like the central nervous system of HR operations, helping businesses of all sizes handle their workforce more efficiently and strategically.
Types of Employee Data Managed
The core purpose of an HRIS is to manage various types of employee information in one centralized system. With the right HRIS training, users can effectively handle the following key data types that an HRIS typically manages:
1. Roles and Job Titles:
Tracks the different positions within the company, including each employee’s specific role, department, and reporting structure. This data is crucial for managing promotions, transfers, and organizational planning.
2. Skills and Qualifications:
Maintains a detailed record of employee skills, certifications, training, and educational background. This helps HR teams identify skill gaps, plan employee development programs, and make informed decisions on promotions or hiring needs.
3. Compensation and Benefits:
Manages salary details, bonuses, and benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and stock options. By keeping this information updated, the HRIS ensures accurate payroll processing and helps with benefits administration.
4. Personal Information:
Stores personal details like contact information, address, emergency contacts, and social security numbers in a secure manner. This ensures that sensitive data is protected and readily available when needed.
5. Performance Metrics:
Tracks employee performance reviews, feedback, and goal progress. This data is valuable for evaluating employee performance management, setting targets, and identifying top performers within the organization.
6. Training Records:
Logs training sessions completed by employees, along with any certifications earned. This helps in planning future training programs and ensuring that employees meet required compliance standards.
By managing these different types of data, an HRIS not only streamlines HR tasks but also provides valuable insights into the workforce, recruitment and strategic decision-making.
Key Features of an HRIS
An HRIS offers a range of features to streamline HR processes, from employee data management and payroll automation to benefits administration and performance tracking. With proper HRIS training, these tools can improve efficiency, reduce errors, and provide valuable insights for strategic decision-making.

1. Employee Data Management
An HRIS centralizes all employee information, making it accessible and manageable in one place. This includes job roles, contact information, work history, and career progression. In fact, companies that implement an HRIS can save up to 22% of their time on administrative tasks related to employee data management, according to a report by HR Technologist.
2. Benefits Administration
Managing employee benefits, such as health insurance, retirement plans, paid time off, and other perks, becomes much more efficient with an HRIS. A study by SHRM found that companies using an HRIS for benefits administration experienced a 40% reduction in administrative errors. The system automates benefit enrollment processes and allows employees to manage their benefits through self-service portals, which increases engagement and ensures they are taking full advantage of the perks provided by the company.
3. Payroll Processing
Payroll processing is one of the most critical functions managed by an HRIS. It automates payroll calculations, taking into account salary, bonuses, overtime, and deductions. According to a KPMG survey, 54% of HR professionals reported that payroll errors decreased significantly after adopting an HRIS, primarily due to the automation of complex calculations and tax compliance.
4. Time and Attendance Management
Tracking employee attendance, working hours, and leave requests is a key feature of an HRIS. The system captures real-time data, ensuring accurate payroll processing and reducing issues related to timekeeping. Research by Software Advice revealed that organizations using HRIS solutions for time and attendance management saw a 45% reduction in payroll processing time.
5. Reporting and Analytics
HRIS systems come equipped with robust reporting and analytics tools that allow HR professionals to generate customized reports and gain insights into various HR metrics. A study by PwC found that 60% of companies improved their decision-making capabilities with data-driven insights from HRIS systems.
By leveraging these features, companies can streamline HR operations, enhance employee experience, and make data-backed decisions that align with organizational goals.
Benefits of Implementing an HRIS
Implementing an HRIS helps automate routine HR tasks, reducing administrative workload and minimizing errors. With effective HRIS training, it also enhances employee engagement, improves compliance, and provides data-driven insights for better workforce planning.
1. Streamlined HR Processes
An HRIS automates repetitive HR tasks, like payroll processing, benefits administration, and employee data management, which significantly reduces the administrative burden on HR teams. According to Forbes, HR professionals spend nearly 50% of their time on routine administrative tasks. With an HRIS, this time can be cut down by up to 30%, allowing HR teams to focus on more strategic activities like talent development and employee engagement.
2. Enhanced Employee Engagement
Modern HRIS platforms offer self-service features that allow employees to update personal information, request leave, access pay stubs, and enroll in benefits programs independently. According to a survey by Gartner, 75% of employees reported higher job satisfaction when they had access to self-service AI recruiting tools.
3. Improved Compliance and Record-Keeping
HRIS systems ensure data accuracy and help maintain compliance with various labor laws and regulations. They provide automated reminders for compliance deadlines and store historical employee records securely. A study by SHRM found that 60% of companies experienced fewer compliance issues after implementing an HRIS, thanks to its real-time data management and reporting capabilities.
4. Strategic HR Support
An HRIS offers valuable insights through analytics and reporting tools, allowing HR teams to align talent management with organizational goals. By analyzing key metrics such as employee turnover rates, performance data, and workforce demographics, HR professionals can make data-driven decisions that support long-term business strategies. According to PwC, 67% of companies stated that using HR analytics improved their strategic workforce planning.
Types of HRIS Systems
HRIS systems can be classified into on-premise and cloud-based solutions, offering flexibility depending on a company’s needs. With appropriate HRIS training, users can optimize these systems, which can also be categorized as operational, tactical, or strategic each serving different HR functions like day-to-day management, workforce planning, and long-term strategy.
On-Premise vs. Cloud-Based Systems
When choosing an HRIS, companies often consider whether to go with an on-premise or cloud-based solution. On-premise HRIS is installed on the company’s local servers, offering greater control and data security but usually involves higher upfront costs and maintenance. On the other hand, cloud-based HRIS is hosted online, providing more flexibility, lower initial costs, and automatic updates, making it a popular choice for many businesses.
Here’s a comparison of the two systems:
| Aspect | On-Premise HRIS | Cloud-Based HRIS |
| Installation | Installed on local servers | Hosted online and accessed via a browser |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost; ongoing maintenance | Lower initial cost; subscription-based |
| Control | Full control over data and software | Limited control; managed by provider |
| Maintenance | Requires in-house IT resources | Automatic updates by the provider |
| Scalability | More complex to scale | Easily scalable to business needs |
| Access | Restricted to on-site network | Accessible from anywhere with internet |
| Data Security | Company manages security measures | Provider implements security protocols |
Operational, Tactical, and Strategic Systems
HRIS systems can be customized to focus on different levels of HR functions: operational, tactical, and strategic. Operational HRIS is designed to handle day-to-day HR activities, like payroll processing, attendance tracking, and managing employee records, making it essential for streamlining routine tasks. Tactical HRIS, on the other hand, supports HR planning and development, including recruitment, training, and performance evaluations. It helps HR professionals manage talent and plan workforce development effectively.
The functionality of an HRIS can vary depending on the needs of the organization. Here’s a breakdown of the three main types:
| Type | Description | Key Focus |
| Operational | Manages everyday HR tasks, including payroll, attendance, and employee records. | Day-to-day HR operations |
| Tactical | Supports HR planning activities such as recruitment, training, and performance evaluations. | HR planning and development |
| Strategic | Provides advanced analytics for workforce planning, identifying talent gaps, and aligning HR with business goals. | Long-term strategic HR management |
HRIS Certifications for Technical Competence
HRIS certifications, such as HRIP, PHR, and SHRM-CP, validate a professional’s expertise in HR technology, HRIS training, and data management. These certifications help HR professionals gain technical competence, enhancing their ability to implement and manage HRIS systems effectively within organizations.
HRIP (Human Resource Information Professional)
The HRIP certification validates a professional’s expertise in HR technology solutions and data management. It covers comprehensive HRIS functions and is ideal for those involved in selecting, implementing, and managing HR software systems in large organizations.
PHR (Professional in Human Resources)
This certification demonstrates technical and operational HR knowledge, including HRIS functionalities. It is suitable for HR professionals who handle various HR tasks, such as payroll, benefits administration, and compliance, using HRIS platforms.
SHRM-CP (Society for Human Resource Management – Certified Professional)
SHRM-CP focuses on HR operations and strategy while emphasizing a strong understanding of HRIS systems. This certification is ideal for professionals involved in strategic workforce planning and using HR analytics to drive business decisions.
aPHR (Associate Professional in Human Resources)
An entry-level certification that introduces HRIS basics and foundational HR concepts. It is perfect for beginners in HR, providing them with the skills to handle data entry, track attendance, and learn basic HRIS functionalities.
Here’s a table summarizing these certifications with examples:
| Certification | Focus Area | Level | Example Use Case |
| HRIP | Comprehensive HRIS functions, HR tech solutions, data management | | Advanced | Implementing a new HRIS for a large organization, ensuring data security, and optimizing HR workflows. |
| PHR | Technical and operational HR knowledge, HRIS functionalities | Intermediate | Managing employee benefits, payroll, and compliance within an existing HRIS. |
| SHRM-CP | HR operations, strategy, HRIS understanding | | Intermediate | Developing strategic workforce planning using HR analytics from the HRIS. |
| aPHR | HRIS basics, foundational HR concepts | Entry-level | Assisting in data entry, tracking attendance, and learning HRIS functionalities in a small business setting. |
HRIS Implementation: Key Steps
Implementing an HRIS can transform the efficiency of HR operations, but it requires careful planning, HRIS training, and execution. Here are the key steps to ensure a smooth transition to your new HR system.
1. Conduct Needs Analysis and Project Planning
The first step in implementing an HRIS is to conduct a thorough needs analysis. This involves assessing the business’s HR requirements, identifying existing pain points, and defining the specific HR processes that need improvement. By engaging with HR teams, managers, and key stakeholders, companies can outline their goals and expectations for the new system.
2. Define Processes and Configure System
Once the requirements are established, the next step is to define HR processes and configure the HRIS to meet the company’s unique workflows. This customization includes setting up modules for employee data management, payroll, attendance tracking, and benefits administration. It’s crucial to customize the system to reflect the organization’s policies, compliance needs, and reporting requirements.
3. Train Users and Deploy System
Successful HRIS implementation hinges on comprehensive training for both HR staff and employees. Providing step-by-step user training helps ensure everyone understands how to use the system’s features effectively. This training can include workshops, manuals, and ongoing support to address any questions or issues.
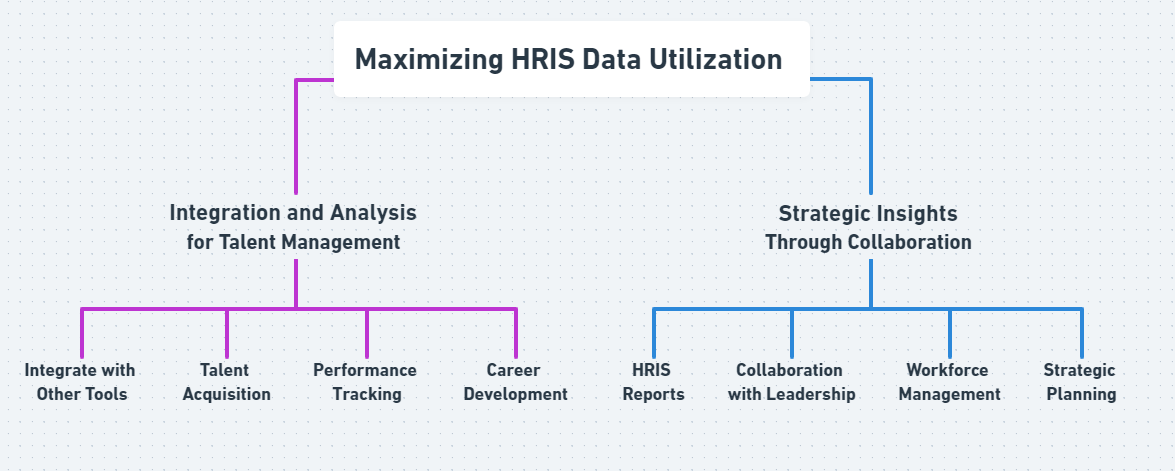
Maximizing HRIS Data Utilization
Effectively utilizing HRIS data, along with proper HRIS training, can optimize talent management by integrating it with other tools to track performance and guide career development. Additionally, HRIS provides valuable insights that foster collaboration with leadership, helping to align workforce strategies with business goals.
Conclusion
An HRIS plays a great role in transforming HR management by streamlining data handling, automating routine tasks, and providing valuable insights for strategic decision-making. With proper HRIS training, from managing employee records to enhancing talent management and driving workforce planning, an HRIS can be a game-changer for any organization’s HR department. Its integration capabilities and analytics tools not only improve operational efficiency but also empower HR teams to align their efforts with the company’s long-term objectives.
Staying updated on the latest HRIS trends and obtaining relevant HR certifications is crucial for HR professionals looking to advance their careers. Continuous learning not only enhances technical competence but also ensures that professionals can fully leverage HRIS to benefit their organizations.
Ready to take your HR management to the next level? Explore cutting-edge HR tech solutions that can revolutionize your HR processes and drive business success. Discover hrtech now!





